Sarcoidosis, or sarcoid,
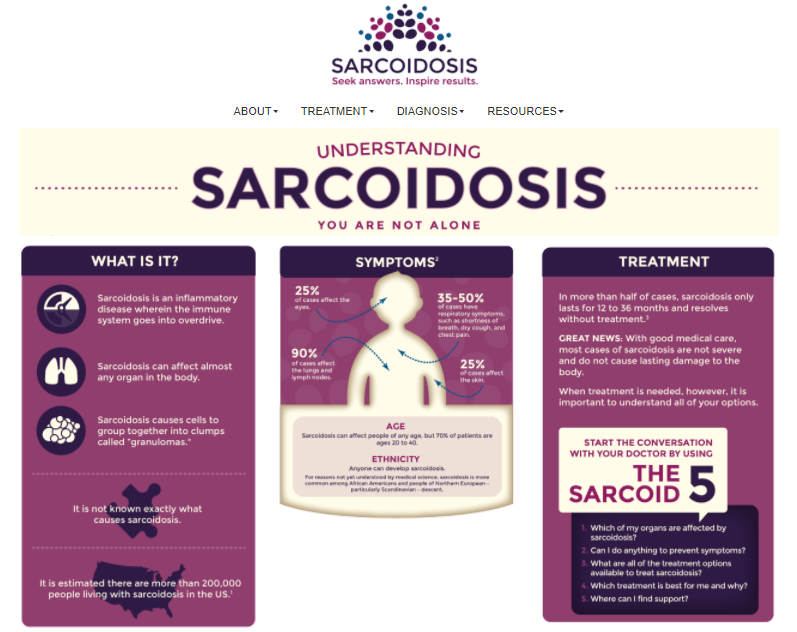
It a disease in which certain inflammatory cells clump together and form nodules known as granulomas in various parts of the body. The most common organs to be affected by sarcoidosis are
the lungs, the skin, and the eyes, although in some people almost any part of the body can be involved. In most cases, the body’s immune system heals the granulomas over a few years. Sometimes, for reasons that are not
understood, this does not happen, and scar tissue is formed. This is called fibrosis and can result in permanent damage.
How many people have sarcoidosis?
Sarcoid is an uncommon condition, although the number of people diagnosed varies from country to country. It is difficult to be sure how many people have sarcoid throughout the world, as many do not know they have it, and sometimes it can be mistaken for other diseases. In the UK, about 3,000 new cases of sarcoidosis are diagnosed each year. It can affect people of any age but is more common in young adults and is slightly more common in women. In some populations, such as Afro-Caribbean, Irish and Swedish people, it can affect up to 60 out of every 100,000 people.
What causes sarcoidosis?
Nobody knows the cause of sarcoid even though much scientific research is being carried out to answer this question. It is also not clear why sarcoid affects different people in different ways.
Some scientists think it may be due to an environmental toxin or a virus that triggers the body to react in a certain way. A person’s individual genetic make-up may also be important.
Despite these uncertainties, if you are a patient who has been diagnosed with sarcoid, you can be reassured by some of the following facts:
The majority of people with sarcoid get better without specific treatment within 12 to 18 months and lead perfectly normal lives
- Sarcoidosis is not infectious; you cannot catch and it cannot be passed between people.
- It is not a form of cancer.
The most common symptoms in people with sarcoidosis include:
- Shortness of breath and a dry cough.
- A flu-like illness with fever, tiredness and joint pains A painful red rash usually occurring on the arms or legs
- Eye irritation and visual problems
- Swollen glands, which can be felt in the neck or around the face


